Fibroids
What are fibroids?
Fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) growths that can form in and around your uterus. They are very common in women aged 20 and over, usually during the reproductive age. Their size and the amount of growth can vary from woman to woman.
What are the symptoms?
In many cases fibroids don’t show any symptoms at all. When symptoms do occur, they depend on a number of factors such as their size and location. They can cause heavy and painful periods, spotting between periods, infertility, difficulty in passing urine or bowel movements, or discomfort during sexual intercourse. Larger fibroids are also known to cause swelling and pressure in the lower abdomen, lower back, bladder or bowel.
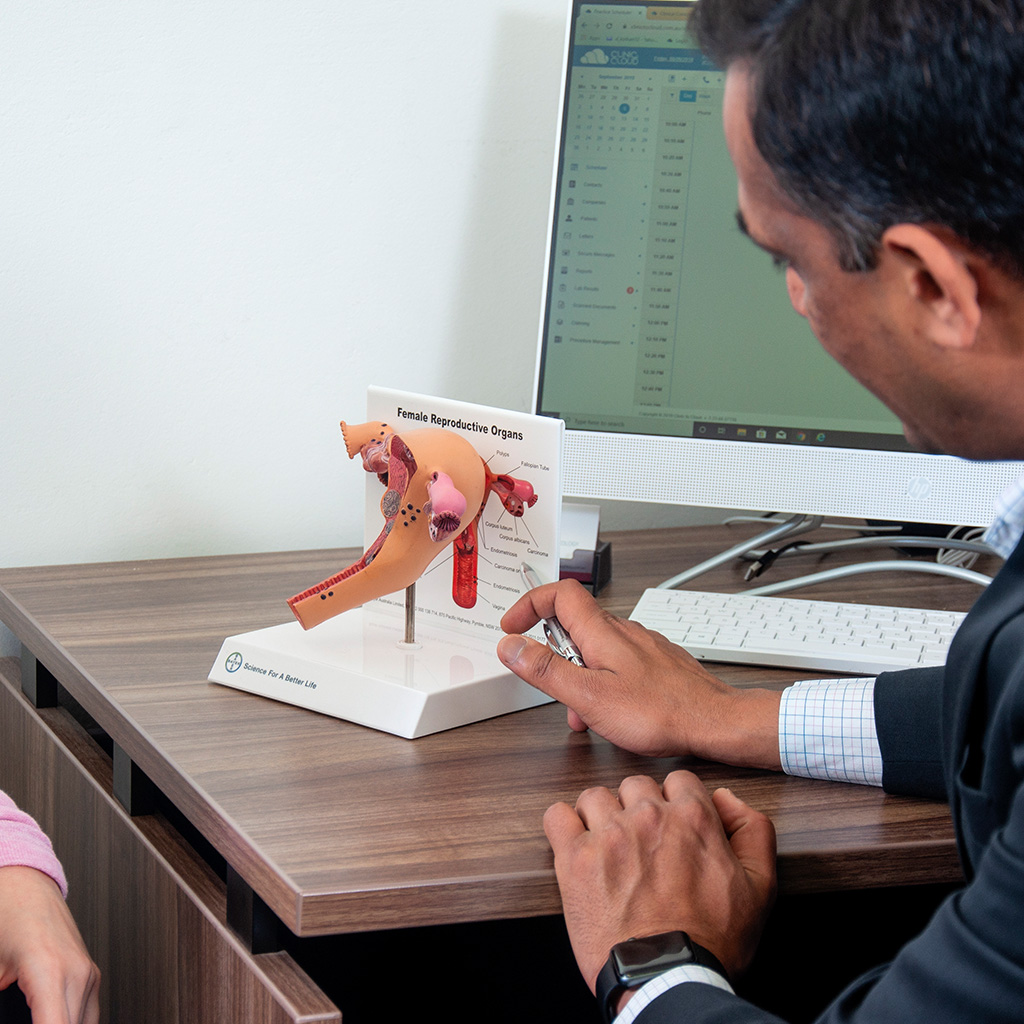


What is the treatment for fibroids?
If fibroids aren’t causing any problems for patients, they generally don’t require treatment. In this case, Dr Kothari would advise on regular monitoring.
For symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, the contraceptive pill may be prescribed for treatment. In some cases, surgery may be required. This would depend on the severity of the symptoms, the size of the fibroids, and the location. Surgical treatments include
- Myomectomy – surgical removal of fibroids from the uterus which can be either be performed by inserting a laparoscope into the uterus through the cervix, through robotic procedures, or via abdominal surgery (this procedure allows the uterus to stay in place and helps to preserve fertility)
- Hysterectomy – this surgery involves the removal of the uterus
Polyps
What are polyps?
A polyp is a small tissue growth, caused by an abnormal growth of cells. They commonly form on the lining of the uterus but can also develop in other areas of the body such as the colon, stomach or bladder.
What are the symptoms?
Polyps of the uterus can cause heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding and infertility, whereas cervical polyps typically show no symptoms but can occasionally cause abnormal bleeding or unusual discharge.
What is the treatment for polyps?
Most polyps are benign (non-cancerous), but it is still recommended that they be removed to prevent further growth and the possibility of becoming malignant. To determine if a polyp is malignant, Dr Kothari will remove the polyp and perform a biopsy by taking a tissue sample from the growth and sending it to a pathologist. Depending on the size and location, polyps are removed by performing a hysteroscopy or laparoscopy.
Cysts
What are cysts?
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled structure that forms in the ovary, commonly found in younger women with regular periods. Most cysts are non-cancerous and can sometimes show no signs of pain or symptoms.
What are the symptoms?
Cysts occasionally show symptoms, including:
- Abdominal bloating
- Regular urination
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Unusual vaginal bleeding
- Pain during sexual intercourse
Cysts can occasionally break open and cause heavy bleeding. This can lead to severe pain with fever, vomiting, and rapid breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect you may have ovarian cysts, you should seek immediate attention from your doctor.
What is the treatment for cysts?
Most ovarian cysts don’t need medical intervention and will disappear naturally. Dr Kothari may perform a physical examination and suggest tests such as an ultrasound or blood tests. If your cysts are diagnosed as non-cancerous, we still recommend regular check-ups to monitor whether the cyst has disappeared or grown.
If the cyst has grown, causes painful symptoms, or is suspected to be cancerous, Dr Kothari may suggest surgery to remove the cyst. Most commonly, a laparoscopy may be performed to remove the cyst (cystectomy) and preserve the ovary or Dr Kothari can remove cysts via robotic surgery. For more complicated cases, the removal of one or both ovaries (oophorectomy) may be required with a laparotomy (open surgery).
